My portfolio
speaks for itself




















PLOTS
Demand forecasting is one of the most important business purposes of companies. With the advent of Data & Analytics, this is made possible by leveraging modelling capabilities from mathematics which are highly adjustable to diverse types of commodities. Below there are some examples of modelling possibilities in which we are heavily specialized.
I - Weather
I - Temperature
Monitoring global and regional temperature variations.
I.II - Air Pressure
Analyzing atmospheric pressure for climate insights.
I.III - Irradiance
Tracking solar radiation to assess energy potential.
I.IV - Cloud Cover
Observing cloud formations to improve forecasting accuracy.
V - Precipitation
Measuring rainfall and snowfall for hydrological studies.
VI - Wind
Assessing wind speed and direction for energy and weather.
II - Electricity Demand
II.I - Business
Electricity consumption by comercial entities such
as offices, retail stores, institutions, etc. These are
strongly tied to working hours and weekday patterns.
II.II - Residential
Household electricity usage. These show peaks in
early morning and evening hours when
people are home.
II.III - Industrial
Electricity demand from manufacturing, processing
and heavy industries. Often show large and relatively
table baseload demand and are sensitive to production
cycles, global economic trends and industrial output.
II.IV - EV Charging
Electricity consumption from charging electric vehicles.
II.V - Photovoltaic
Electricity generation rom solar photovoltaic
systems, which is often modelled as negative
demand since we normally analyze net load.
III - Traffic Demand
III.I - Road Demand
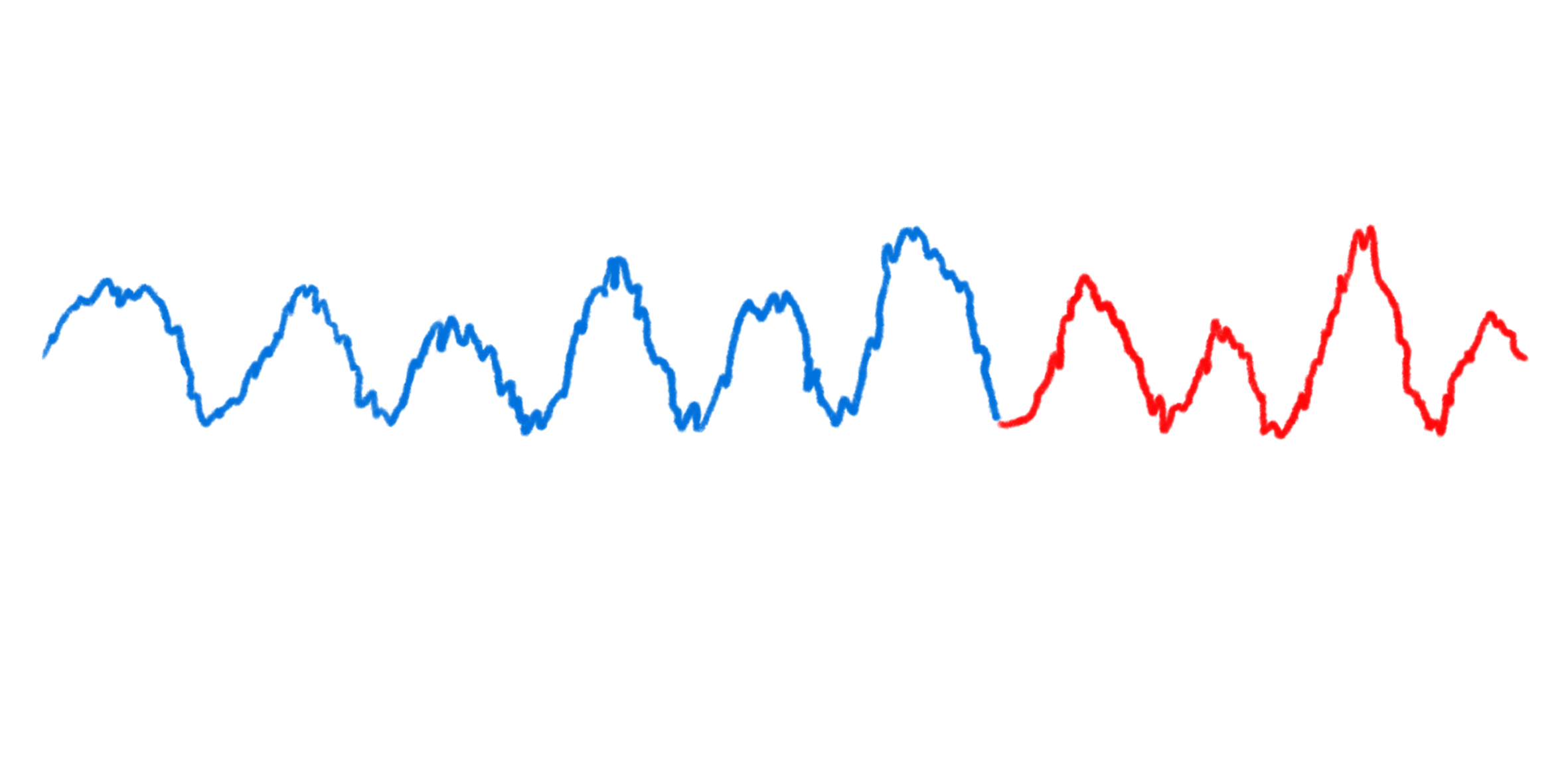
Represents the total volume or intensity of vehicle
traffic on public roads, typically measured as the
number of vehivles per unit time.
III.II - Shuttle Demand

Predicts shuttle availability and measures the
frequency of shuttle vehicle operations.
IV - Logistic Demand
Logistic Demand
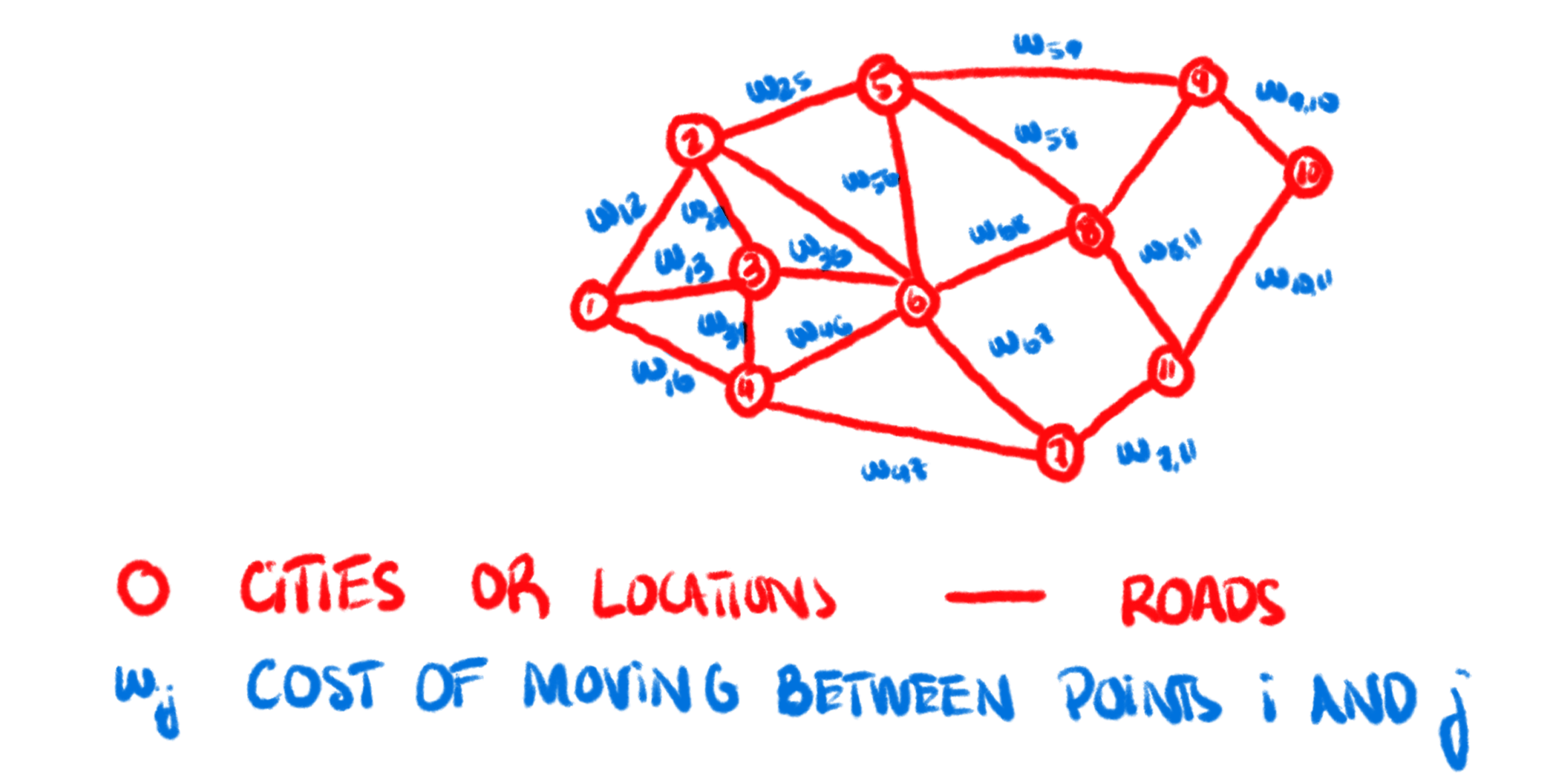
Models are tailored to predict industrial logistics
representing the volume of freight and goods
transport activity across roads.
V - Clustering
V.I - Fraud Detection
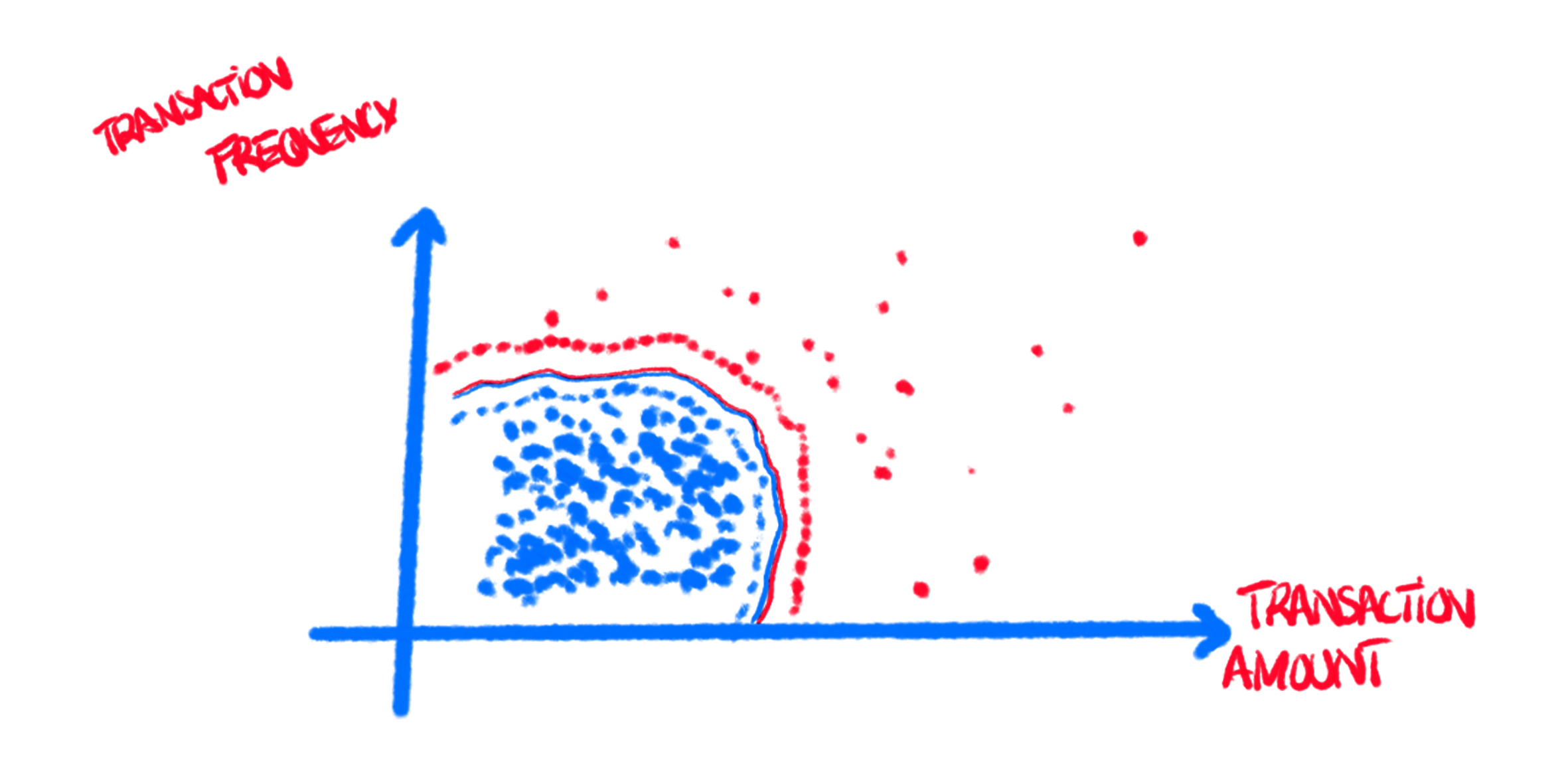

Identifying anomalies and preventing fraudulent activity
in financial and transactional systems.
V.II - Customer Segmentation
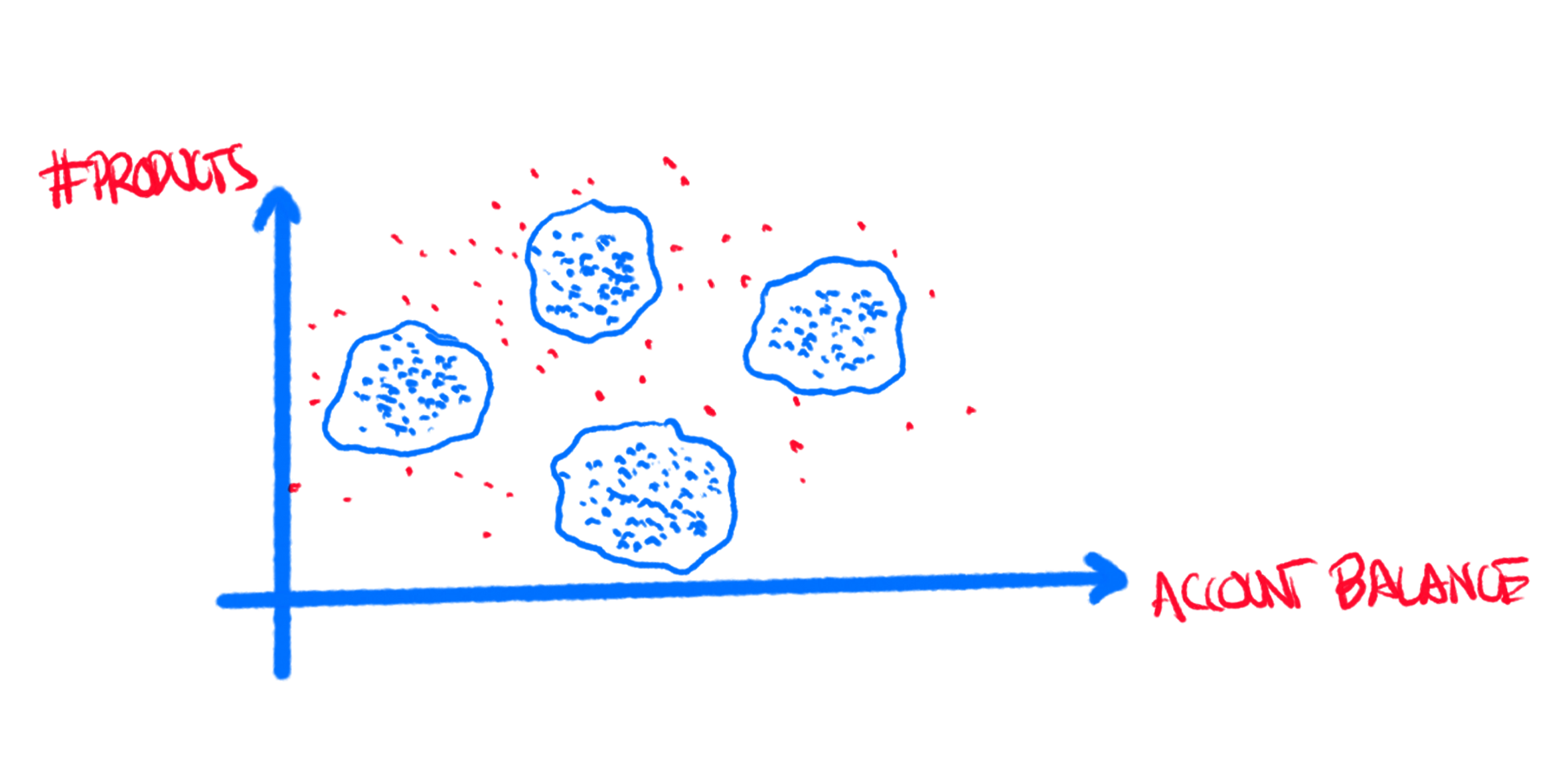
Grouping users by behavior and characteristics to tailor
marketing and product strategies.
VI - Trading
VI.I - Labelling
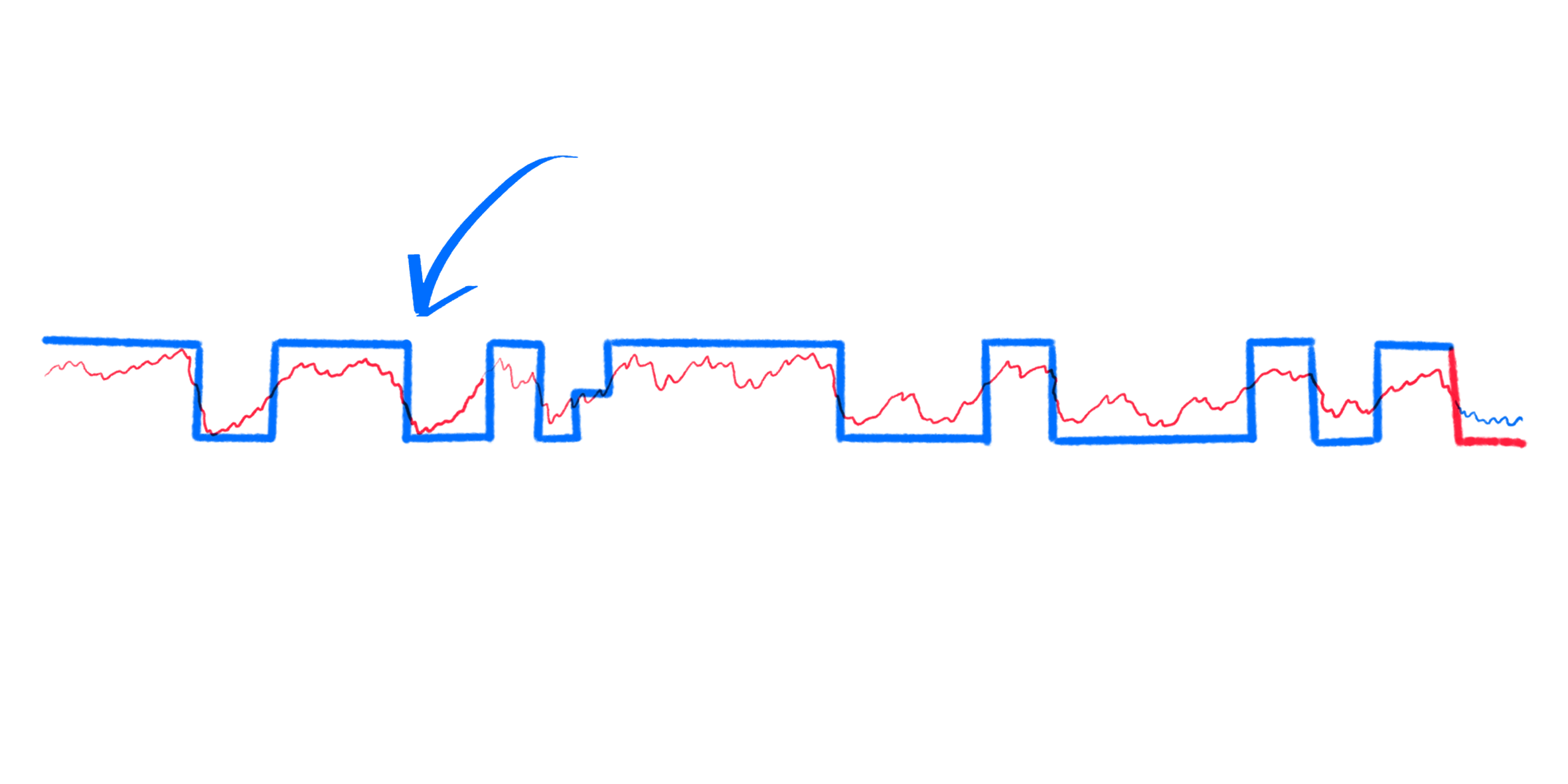
Labelling is the first step of a trading algorithm
and learns how to position in the market based
on barrier thresholding or trend scanning methods.
VI.II - Probabilistic Forecasting
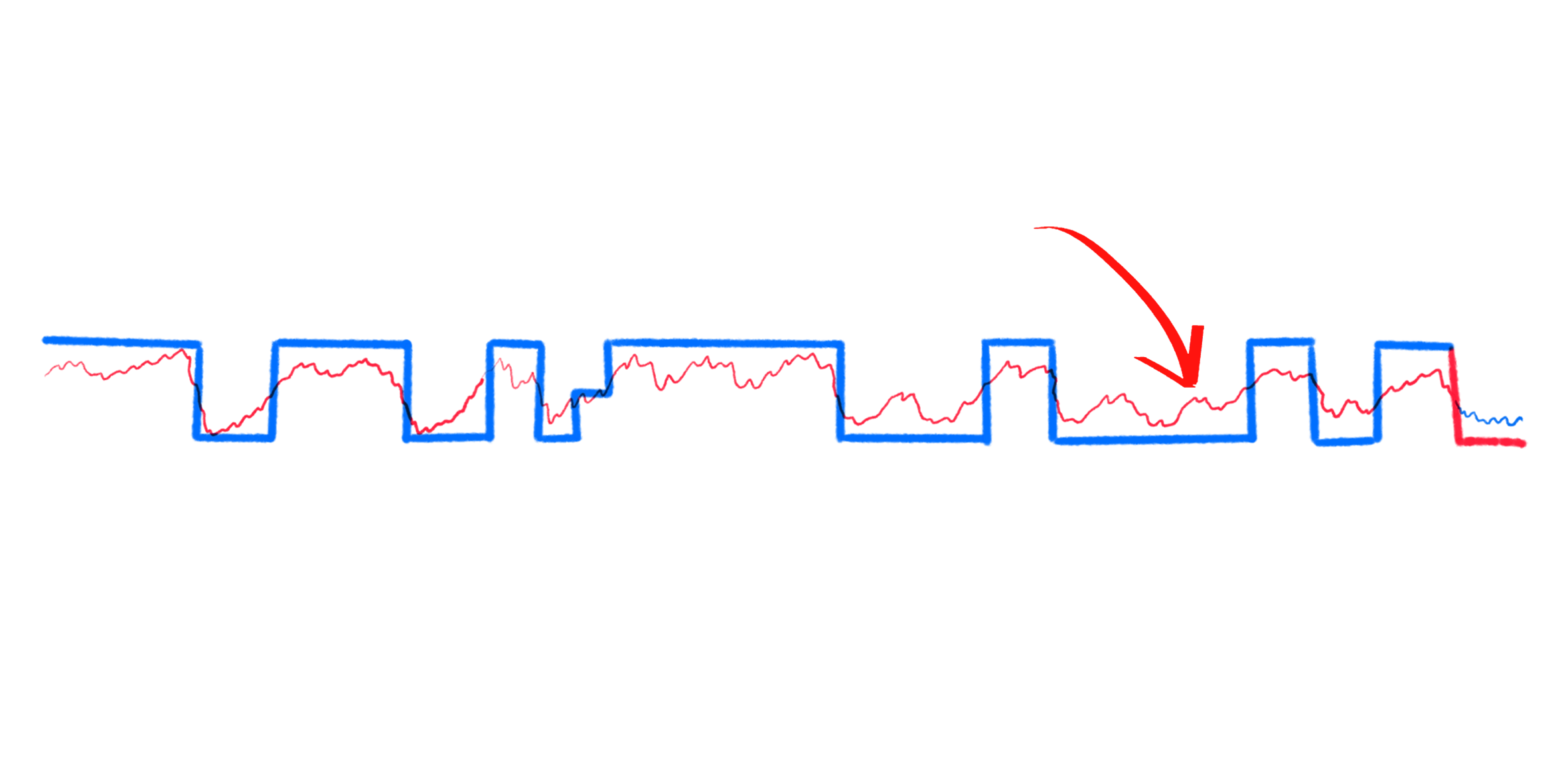
Using Monte Carlo methods, we can sample from
the expected probability distribution and derive
a probability value for the increase in price.
VI.III - Price Forecasting
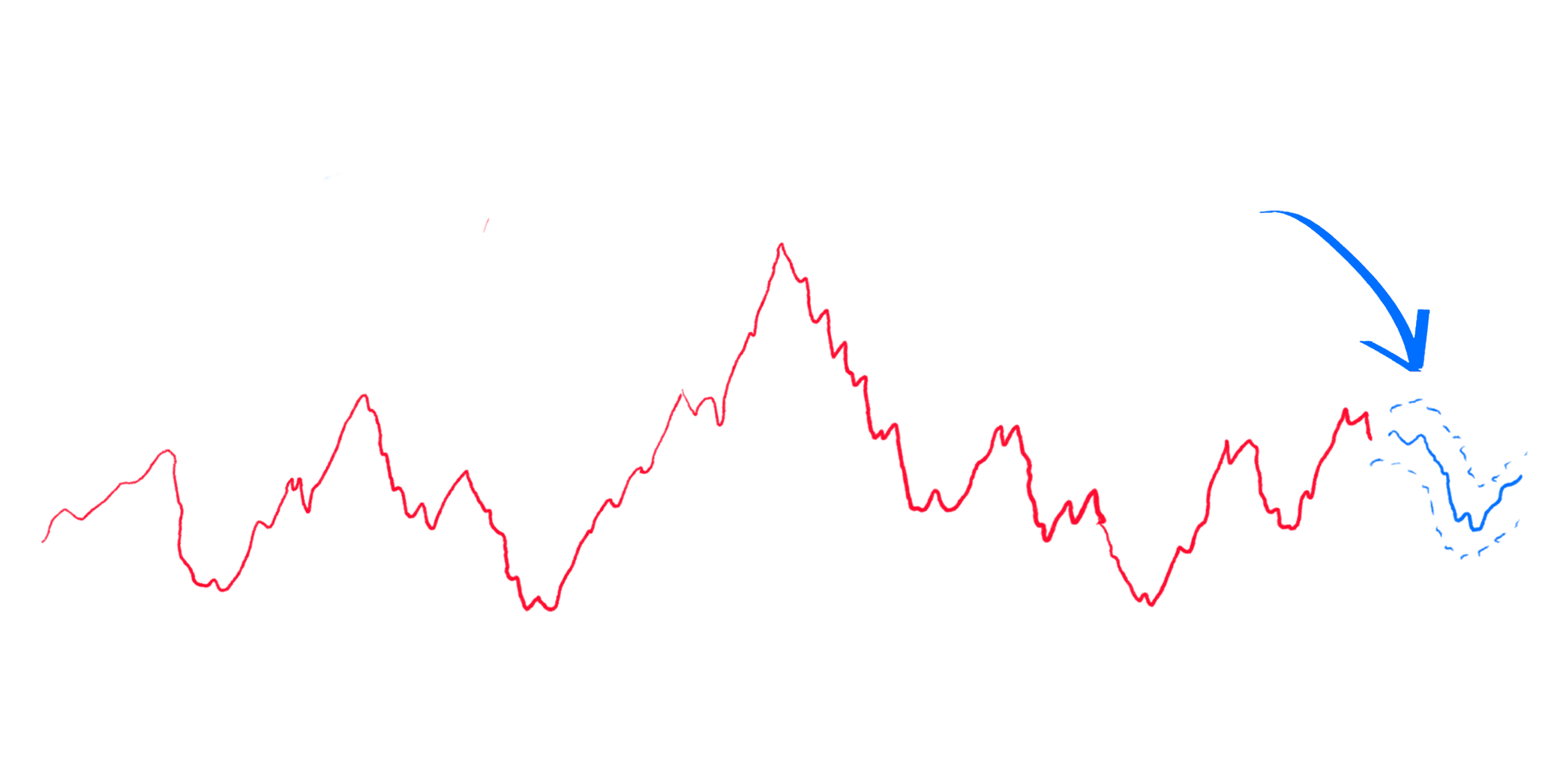
Based on the probability forecast we are able
to derive an expected future probabilistic
distribution for price, indeed leading to a more
informed forecast.
VII - Custom Neural Network
VII.I - Custom Neural Network Archithectures

Models are tailored to predict industrial logistics
representing the volume of freight and goods
transport activity across roads.
